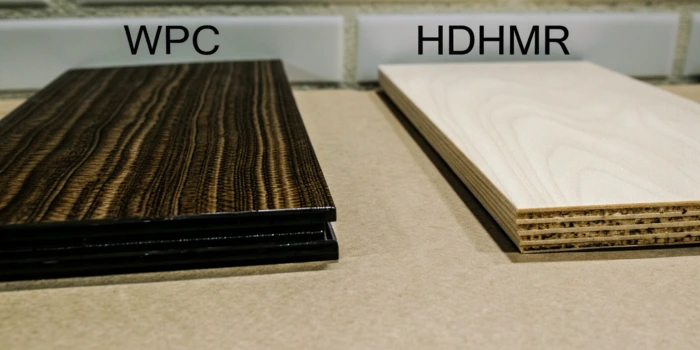
When it comes to choosing the right material for furniture, flooring, or other interior applications, two popular options are WPC (Wood Plastic Composite) and HDHMR (High-Density High Moisture Resistant) boards. But, which is the best option for your specific needs?
In this article, we’ll compare WPC vs HDHMR across various aspects, including price, applications, components, types, and design to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding The Basics Of WPC vs HDHMR
WPC (Wood Plastic Composite) is a durable, moisture-resistant material made from a blend of wood fibers and plastic, ideal for outdoor applications. HDHMR (High-Density High Moisture Resistant), on the other hand, is a dense, moisture-resistant board designed for indoor use in areas with high humidity, such as kitchens and bathrooms.
What Is WPC?
WPC stands for Wood Plastic Composite, a material made by blending wood fibers with plastic. This combination makes WPC strong, durable, and resistant to various environmental factors. It is commonly used in furniture, decking, and flooring applications.
What Is HDHMR?
HDHMR, or High-Density High Moisture Resistant, is a type of engineered wood that’s specially designed to withstand high moisture environments. It has a dense structure, which makes it highly durable and resistant to water damage. HDHMR is often used in areas with high humidity, such as bathrooms and kitchens.
What Are The Key Differences WPC vs HDHMR?
The applications of WPC (Wood Plastic Composite) and HDHMR (High-Density High Moisture Resistant) boards differ significantly based on their properties and the specific requirements of the project. Here’s a detailed breakdown of where each material excels:
Key Differences Of WPC
- Decking
- Why WPC? WPC is an excellent choice for decking because of its resistance to moisture, UV rays, and weather conditions. It doesn’t warp, crack, or degrade like natural wood, making it a durable and low-maintenance option for outdoor spaces.
- Benefits: It offers the aesthetic appeal of wood while being much easier to maintain, perfect for outdoor decks exposed to sunlight and rain.
- Flooring
- Why WPC? WPC is increasingly used for flooring in areas with moderate humidity or for outdoor flooring solutions. It offers a balance of strength, durability, and water resistance, making it a good alternative to traditional wood flooring.
- Benefits: WPC flooring is resistant to moisture, making it suitable for areas like balconies, patios, and entryways where natural wood might deteriorate.
- Outdoor Furniture
- Why WPC? WPC is ideal for outdoor furniture because it combines the natural look of wood with the strength and durability of plastic. It is resistant to weathering, moisture, and insects, making it a long-lasting option for garden furniture.
- Benefits: It’s low-maintenance, durable, and resistant to fading from UV exposure, making it perfect for furniture exposed to the elements.
- Wall Paneling
- Why WPC? WPC is often used for wall paneling in both interior and exterior applications. It’s resistant to moisture and can withstand the elements when used outdoors, while also being easy to clean and maintain indoors.
- Benefits: It offers a stylish, modern look and is available in a variety of textures and finishes. Its moisture resistance makes it suitable for areas like bathrooms or kitchens.
- Fencing
- Why WPC? WPC is a popular choice for outdoor fencing due to its durability and weather resistance. It can withstand exposure to rain, wind, and sun without rotting or warping like traditional wood.
- Benefits: It is easy to maintain and provides a long-lasting, aesthetically pleasing alternative to wood fences. It’s especially useful in areas with fluctuating weather conditions.
Key Differences Of HDHMR
- Kitchen Cabinets
- Why HDHMR? HDHMR is an ideal material for kitchen cabinets due to its high moisture resistance. Kitchens are high-moisture environments, and HDHMR can resist swelling, warping, and fungal growth, which are common issues with wood-based materials in such settings.
- Benefits: It ensures longevity and maintains structural integrity in humid kitchen environments, where traditional wood materials may deteriorate over time.
- Bathroom Vanities
- Why HDHMR? Bathrooms experience high humidity and frequent water exposure, making HDHMR the perfect material for vanities. It resists moisture and prevents warping, ensuring that the vanity maintains its shape and appearance over time.
- Benefits: HDHMR’s moisture resistance helps to avoid the common issues of swelling and mildew, making it ideal for bathroom furniture and fixtures.
- High-Moisture Areas
- Why HDHMR? HDHMR is specifically designed for areas with high moisture content, such as laundry rooms, basements, and other damp environments. It is resistant to water damage and maintains its integrity in these challenging conditions.
- Benefits: It is more durable than standard MDF or plywood in areas prone to moisture, offering superior protection against humidity-related damage.
- Furniture
- Why HDHMR? HDHMR is often used for indoor furniture, especially in areas with high humidity. It’s a strong and moisture-resistant material that helps ensure furniture longevity and maintains its aesthetic appeal.
- Benefits: It offers a high-quality finish and is resistant to moisture, making it a great option for furniture that needs to withstand varying indoor conditions.
- Doors And Window Frames
- Why HDHMR? HDHMR is ideal for doors and window frames in environments where moisture is a concern. It resists warping, swelling, and fungal growth, which are common issues with traditional wood materials in damp areas.
- Benefits: The moisture resistance and high density of HDHMR ensure that doors and window frames maintain their structural integrity and appearance, even in humid conditions.
WPC vs HDHMR Components
WPC boards consist of wood fibers, plastic (usually PVC or polypropylene), and additives. The plastic content makes WPC boards resistant to water, insects, and termites, which is ideal for outdoor and semi-outdoor applications.
HDHMR, on the other hand, is made from wood fibers, resins, and chemicals that enhance its density and moisture resistance. This unique combination makes HDHMR particularly useful in high-humidity and high-traffic areas.
WPC vs HDHMR Board Price
When comparing WPC vs HDHMR board price, WPC tends to be more affordable. The manufacturing process for WPC is cost-effective, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. On the other hand, HDHMR is slightly more expensive due to its high-density and moisture-resistant properties.
Although the price difference exists, it’s important to consider the long-term durability and specific needs of your project before making a decision.
Types Of WPC vs HDHMR
When choosing between WPC (Wood Plastic Composite) and HDHMR (High-Density High Moisture Resistant) boards, it’s important to understand the different types of each material, as they are designed for specific applications. Here’s an elaboration on the various types of WPC and HDHMR and their unique features:
Types of WPC (Wood Plastic Composite)
1. Foam-Based WPC
- Core Features: Foam-based WPC is made by combining wood fibers or flour with plastic, but the key difference is that it incorporates a foam core. This makes the material lightweight, yet it retains the durability and weather resistance typical of WPC.
- Applications: Because of its light weight, foam-based WPC is easy to handle, making it a popular choice for applications like decking, outdoor furniture, and cladding. It is also used for decorative elements, as the foam structure allows for easy cutting and shaping.
- Benefits: The foam core provides excellent insulation properties and is cost-effective, making it an attractive choice for projects where weight and ease of handling are important. It’s also resistant to termites and rot, which makes it a great alternative to traditional wood in outdoor settings.
- Drawbacks: Foam-based WPC may not be as durable as solid WPC for heavy-duty applications like flooring, as the foam core may not provide the same level of strength.
2. Solid WPC
- Core Features: Solid WPC is denser and more robust than foam-based WPC. It is created by combining wood fibers and plastic without the foam core, resulting in a more solid and heavy material. This gives it a higher load-bearing capacity and makes it suitable for more demanding applications.
- Applications: Solid WPC is commonly used for flooring, wall panels, and other structural applications where strength and durability are critical. It can withstand heavy foot traffic and the wear and tear associated with interior use.
- Benefits: The density of solid WPC gives it enhanced durability and strength, making it ideal for high-traffic areas or areas that require more robust materials. It also provides a more solid feel, closer to natural wood, and is highly resistant to moisture and UV damage.
- Drawbacks: Solid WPC is heavier and more expensive than foam-based WPC, which can make it less ideal for large-scale outdoor projects where weight and cost are a concern.
3. Hollow WPC
- Core Features: Hollow WPC is designed with a hollow core structure, which makes it lighter and more cost-effective than solid WPC. Despite the hollow core, it still retains the durability and weather resistance that WPC is known for.
- Applications: Hollow WPC is commonly used for outdoor applications like fencing, decking, and cladding. It is particularly useful in situations where weight is a concern, such as in large outdoor areas or for DIY projects.
- Benefits: The hollow core makes it more affordable and easier to transport and handle. It’s also lighter, making it easier to install. The hollow design can also provide additional insulation, reducing noise and improving thermal performance.
- Drawbacks: While the hollow core reduces weight and cost, it also means the material may not be as strong as solid WPC. It is less suitable for areas where high durability and structural strength are required.
Types Of HDHMR (High-Density High Moisture Resistant)
Discover the key differences, durability, and benefits of WPC vs HDHMR for construction, furniture, interior design, and home improvement applications. Learn about the types of HDHMR and their uses.
1. Standard HDHMR
- Core Features: Standard HDHMR is the basic form of this material, made by combining high-density wood particles with moisture-resistant resins. It is engineered to withstand moderate moisture levels, but it doesn’t have the specialized properties of fire or extreme moisture resistance.
- Applications: Standard HDHMR is most commonly used in furniture manufacturing, cabinetry, and paneling. It is also used for general interior applications where moisture resistance is important but not critical.
- Benefits: Standard HDHMR offers excellent durability and moisture resistance compared to regular MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) or plywood. It’s a more cost-effective solution for indoor applications that require moisture resistance without needing specialized properties.
- Drawbacks: While resistant to moisture, it may not be as effective in areas with extremely high humidity or in applications where fire resistance is required.
2. Fire-Resistant HDHMR
- Core Features: Fire-resistant HDHMR is an upgraded version of standard HDHMR, with added fire-retardant chemicals incorporated into the board during manufacturing. This makes it resistant to flames and heat, helping to slow down the spread of fire in case of an emergency.
- Applications: Fire-resistant HDHMR is commonly used in commercial and industrial settings, including office buildings, schools, and hospitals, where fire safety is a top priority. It is also used in applications like door cores, wall panels, and partitioning systems that require fire resistance.
- Benefits: This type of HDHMR provides an additional layer of safety, making it ideal for environments where fire hazards are a concern. It combines the moisture resistance of HDHMR with fire-resistant properties, offering a comprehensive solution for building interiors.
- Drawbacks: Fire-resistant HDHMR is typically more expensive than standard HDHMR due to the added fire-retardant properties. It may also be heavier and more difficult to handle than other types of HDHMR.
3. Moisture-Resistant HDHMR
- Core Features: Moisture-resistant HDHMR is specifically designed for environments with high moisture levels, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and laundry rooms. It is manufactured with special resins that prevent water absorption and protect the material from swelling or warping.
- Applications: This type of HDHMR is ideal for areas exposed to constant moisture, such as kitchen cabinets, bathroom vanities, and other furniture items that are frequently in contact with water or high humidity.
- Benefits: Moisture-resistant HDHMR offers superior protection against the damaging effects of water and humidity, ensuring long-lasting performance in wet environments. It also resists fungal growth, which is common in areas with high moisture.
- Drawbacks: While moisture-resistant, HDHMR may not be suitable for direct water exposure, such as in areas with frequent flooding. It is also generally more expensive than standard HDHMR due to its specialized moisture-resistant properties.
WPC vs HDHMR Design And Aesthetic Appeal
Discover the key differences, durability, and benefits of WPC vs HDHMR for construction, furniture, interior design, and home improvement applications. Explore WPC vs HDHMR design and aesthetic appeal.
WPC Design
WPC boards offer a wide range of design possibilities, including wood-like textures and finishes. This makes them a great option for those looking for the appearance of wood with the benefits of plastic’s durability. WPC is available in various colors and designs, giving you the flexibility to choose the perfect match for your project.
HDHMR Design
HDHMR offers a more refined and polished appearance, often resembling traditional wood. It can be painted, laminated, or veneered for enhanced aesthetic appeal. The high-density nature of HDHMR allows it to hold finishes and coatings better, making it a popular choice for furniture and cabinetry where design is a key consideration.
WPC vs HDHMR Durability And Resistance
Explore the durability and resistance of WPC vs HDHMR for construction, furniture, interior design, and home improvement applications. Learn how each material withstands wear and moisture.
WPC Durability
WPC is known for its high resistance to water, termites, and weather conditions. It does not warp or crack like natural wood, making it a long-lasting option for outdoor and semi-outdoor applications. However, it may not be the best choice for high-moisture areas, such as bathrooms, where HDHMR excels.
HDHMR Durability
HDHMR is incredibly durable, especially in high-humidity environments. Its high density and moisture resistance make it highly durable in areas like kitchens and bathrooms, where conventional plywood or MDF may fail. HDHMR also resists scratches and dents, ensuring your surfaces remain smooth and pristine for years.
WPC vs HDHMR: Which Is Best For Your Project?
The choice between WPC (Wood Plastic Composite) and HDHMR (High-Density High Moisture Resistant) boards can significantly impact the outcome of your project. Each material has unique properties that make it more suitable for different applications. Here’s an elaboration of the key considerations:
1. Outdoor Projects: WPC vs HDHMR
- WPC: Wood Plastic Composite is an ideal choice for outdoor applications like decking, fencing, and garden furniture. WPC is a blend of wood fibers and plastic, which gives it superior resistance to moisture, UV rays, and weather conditions. Unlike natural wood, WPC won’t warp, crack, or degrade under exposure to the elements, making it a long-lasting option for outdoor environments.
- HDHMR: While HDHMR is moisture-resistant, it is not as suitable for outdoor projects as WPC. HDHMR is designed for indoor use, particularly in high-humidity areas. Its resistance to moisture makes it a good option for spaces like kitchens and bathrooms, but it may not perform as well as WPC when exposed to direct sunlight or rain.
2. High-Humidity Areas: WPC vs HDHMR
- HDHMR: High-density High Moisture Resistant boards are specifically engineered for areas with high moisture content. They are ideal for environments like kitchens, bathrooms, and laundry rooms, where the material is frequently exposed to water or high humidity. HDHMR is resistant to warping, swelling, and fungal growth, making it a durable option for moisture-prone areas.
- WPC: Although WPC is moisture-resistant, it is more suitable for outdoor projects. In high-humidity indoor environments, HDHMR is the better option as it provides better protection against moisture-related damage. WPC can still be used in areas with moderate humidity but may not be as effective as HDHMR in more extreme conditions.
3. Budget: WPC vs HDHMR
- WPC: When cost is a primary concern, WPC is the more budget-friendly choice. It offers an affordable alternative to natural wood and other composite materials while providing a range of benefits, such as durability and low maintenance. WPC’s cost-effectiveness makes it a popular choice for large-scale projects like decking or fencing, where you need to cover a large area without exceeding the budget.
- HDHMR: HDHMR tends to be more expensive than WPC, especially for applications that require high moisture resistance. While it offers superior durability in specific indoor applications, the higher cost may not justify its use in projects where moisture resistance is not a critical factor. For those on a tighter budget, WPC may be the more economical option.
4. Design Preferences: WPC vs HDHMR
- HDHMR: If your project requires a more wood-like appearance, HDHMR is an excellent choice. It mimics the look and feel of natural wood, making it suitable for interior applications where aesthetics are important.
HDHMR can be easily painted or laminated, allowing for customization in terms of color and texture. It’s often used for furniture, cabinetry, and paneling, where the visual appeal of wood is desired without the drawbacks of natural wood. - WPC: While WPC also offers a wood-like appearance, it may not have the same depth and richness as HDHMR. WPC is available in a variety of finishes, but it may lack the intricate grain patterns and natural texture that HDHMR provides. However, WPC can still be a good choice for projects where the look of wood is desired but the material needs to be more durable and weather-resistant.
Conclusion
The decision between WPC vs HDHMR largely depends on your specific needs. If you’re working on an outdoor project, WPC’s resistance to moisture and cost-effectiveness makes it a great choice. However, if your project involves areas with high humidity, such as kitchens or bathrooms, HDHMR’s superior moisture resistance and durability make it the better option. Understanding the strengths and applications of both materials will help you make the right choice for your project.
Frequently Asked Questions? (FAQs)
Which Is Better WPC vs HDHMR?
Both materials have their advantages. WPC is better for outdoor and low-budget projects, while HDHMR is ideal for high-moisture areas like kitchens and bathrooms. The best choice depends on your project’s needs
What Is The Difference Between WPC And HDHMR?
WPC is generally less expensive than HDHMR. The cost difference varies based on the thickness and brand of the material, but WPC tends to be a more affordable option.
Can WPC Be Used For Furniture?
Yes, WPC can be used for furniture, particularly outdoor furniture. However, for indoor furniture or areas with high moisture, HDHMR would be a better choice due to its durability and resistance to moisture.
Is HDHMR Suitable For Outdoor Use?
HDHMR is not ideal for outdoor use, especially in direct exposure to the elements. WPC is the better option for decking, fencing, and other outdoor application